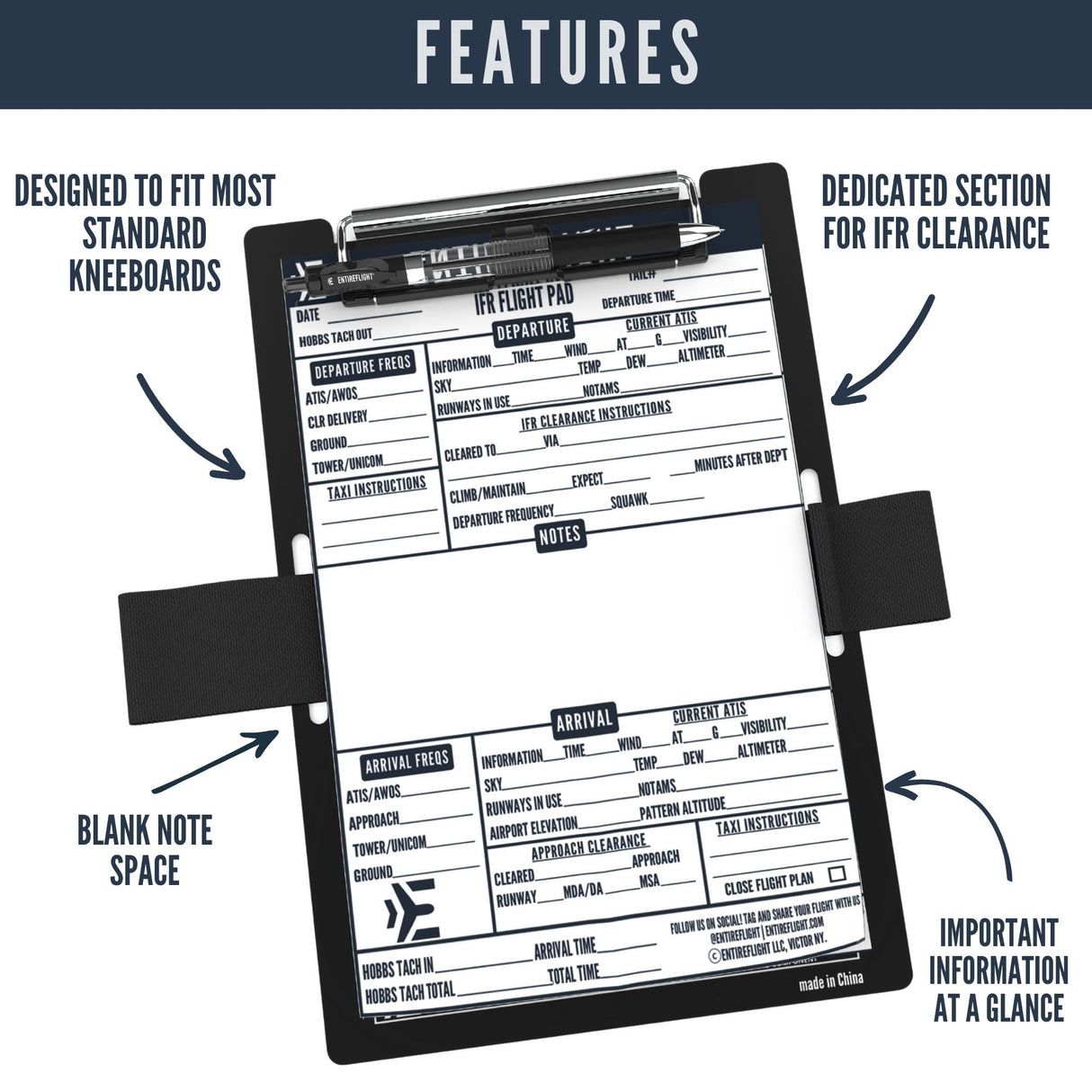
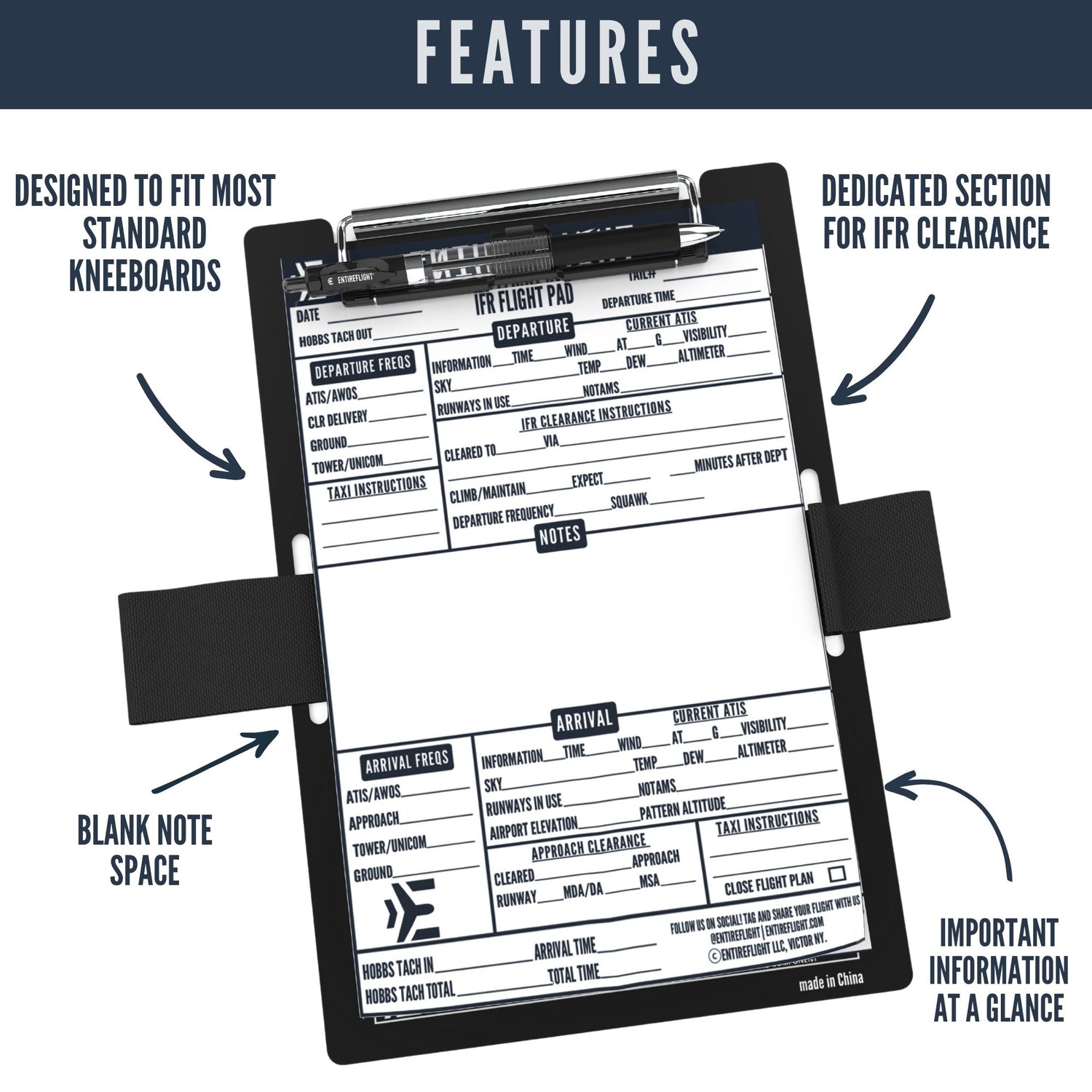
Ground reference maneuvers are an essential part of flight training. These maneuvers involve using external references on the ground to maintain precise control of an aircraft's position and altitude.
Ground reference maneuvers are designed to teach pilots how to maintain accurate altitude and position while flying in relation to the ground. These maneuvers involve using visual cues on the ground to maintain a consistent altitude and heading. Pilots must be able to accurately judge the distance and speed of the aircraft in relation to the ground to perform these maneuvers correctly.
Join us as we dive deeper into this topic and enrich your aviation knowledge. Keep reading.
What are Ground Reference Maneuvers?
Ground reference maneuvers refer to a set of flight maneuvers that a pilot performs while observing and referencing the ground below. These maneuvers are essential for pilots to develop a better understanding of their aircraft's handling characteristics, especially when flying at low altitudes.
Ground reference maneuvers are important for pilots to master because they help in developing the necessary skills to fly safely in and around airports, as well as in non-towered airspace. These maneuvers also help pilots to better understand the effects of wind and other environmental factors on their aircraft.
FAA Regulations
The FAA requires pilots to demonstrate proficiency in ground reference maneuvers during their flight training. According to the FAA's Practical Test Standards (PTS), pilots are required to demonstrate proficiency in the following ground reference maneuvers:
- S-Turns Across a Road
- Turns Around a Point
- Rectangular Course
The FAA also requires pilots to understand the airspace and air traffic regulations that apply to ground reference maneuvers. Pilots must be aware of the minimum safe altitudes and the required distances from people and property when performing these maneuvers.
Key Elements of Ground Reference Maneuvers
When it comes to ground reference maneuvers, there are several key elements that you need to keep in mind. These elements are crucial to ensuring that you are able to complete the maneuver safely and accurately. Here are the main elements you need to focus on:
Altitude
Maintaining the correct altitude is critical during ground reference maneuvers. You need to keep a constant eye on your altimeter to ensure that you are flying at the correct height. Deviating from the correct altitude can cause your ground reference maneuver to fail.
Airspeed
Controlling your airspeed is also important during ground reference maneuvers. You need to maintain a consistent airspeed to ensure that you are able to maintain the correct bank angle and ground speed. Flying too fast or too slow can cause problems with your maneuver.
Wind Direction
The wind direction will have a significant impact on your ground reference maneuver. You need to be aware of the wind direction and adjust your maneuver accordingly. Failing to account for wind direction can cause your maneuver to fail.
Wind Correction
Wind correction is another critical element of ground reference maneuvers. You need to adjust your bank angle and heading to compensate for the wind. Failing to make the necessary corrections can cause your maneuver to drift off course.
Bank Angle
The bank angle is the angle at which your aircraft is tilted during the maneuver. You need to maintain a consistent bank angle to ensure that you are able to maintain the correct ground speed and heading. Exceeding the maximum bank angle can cause your maneuver to fail.
Ground Speed
Ground speed is the speed at which your aircraft is moving relative to the ground. You need to maintain a consistent ground speed to ensure that you are able to complete the maneuver accurately. Deviating from the correct ground speed can cause your maneuver to fail.
Types of Ground Reference Maneuvers
Ground reference maneuvers are a key part of flight training that help pilots develop their skills in flying a plane. There are several types of ground reference maneuvers that you should be familiar with.
Turns Around a Point
Turns around a point is a type of ground reference maneuver where you fly in a circular pattern around a fixed point on the ground. This maneuver is used to practice maintaining a constant radius around the point while adjusting for wind drift. It is also a good way to practice using your rudder to maintain coordination during the turn.
S-Turns
S-turns are a type of ground reference maneuver where you fly in a zigzag pattern over a straight line on the ground. This maneuver is used to practice maintaining a constant distance from a line on the ground while adjusting for wind drift. It is also a good way to practice using your rudder to maintain coordination during turns.
Rectangular Course
A rectangular course is a type of ground reference maneuver where you fly a rectangular pattern around a fixed point on the ground. This maneuver is used to practice maintaining a constant distance from the ground while adjusting for wind drift. It is also a good way to practice using your rudder to maintain coordination during turns.
Aircraft Control During Ground Reference Maneuvers
In this section, we will discuss the different flight control pressure inputs required to maintain proper aircraft control during ground reference maneuvers:
- Roll: To keep a steady bank angle during ground reference maneuvers, use the ailerons. Increase bank angle by pushing the aileron in the direction of the turn and decrease it by pushing the opposite aileron. Maintain this angle for a consistent turn radius.
- Rudder: Control the aircraft's yaw with the rudder during ground reference maneuvers to maintain a constant heading. Turn by pressing the rudder in the desired direction and keep a straight heading by using the opposite rudder. Coordinate the rudder with the ailerons to keep your bank angle steady.
- Aileron: Manage the aircraft's roll using the ailerons during ground reference maneuvers. Increase bank angle with the aileron in the turn's direction and decrease it with the opposite aileron. Coordinate aileron and rudder inputs to maintain a constant heading.
- Pitch: Utilize the elevator for pitch control during ground reference maneuvers to maintain a consistent altitude. Increase altitude with back pressure on the elevator and decrease it with forward pressure. Always ensure a steady airspeed while adjusting pitch.
Practical Application of Ground Reference Maneuvers
When are ground reference maneuvers most useful? In this section, we’ll discuss the scenarios where they are most applicable and helpful in flight.
Takeoff
During takeoff, ground reference maneuvers can be used to maintain a straight and steady path. By using a ground feature such as a road or fence line as a reference point, you can ensure that you are not drifting to the left or right. This is particularly important in crosswind conditions. By keeping the reference point in line with the aircraft's longitudinal axis, you can maintain a straight takeoff path.
Landing
Ground reference maneuvers can also be used during landing to ensure a smooth and controlled touchdown. By using a ground feature such as a runway or taxiway as a reference point, you can ensure that you are approaching the runway at the correct angle and speed. This is particularly important when landing in gusty or crosswind conditions. By keeping the reference point in line with the aircraft's longitudinal axis, you can maintain a straight and stable approach.
Emergency Procedures
In the event of an engine failure, ground reference maneuvers can be used to help you find a suitable landing spot. By using a ground feature such as a road or field as a reference point, you can ensure that you are maintaining a safe altitude and speed while searching for a suitable landing spot. Once you have identified a suitable spot, you can use ground reference maneuvers to ensure a safe and controlled emergency landing.
Common Errors and Corrections in Ground Reference Maneuvers
Like any other flight maneuver, ground reference maneuvers can be challenging, and there are common errors that you should avoid. Let’s discuss.
Drift Correction
Drift correction is essential in ground reference maneuvers. Failure to correct for drift can result in significant deviations from your intended path. The following are common errors and corrections in drift correction:
- Failure to identify wind direction: Before you start your maneuver, you should identify the wind direction. Failure to do so can result in incorrect drift correction. You can use visual cues such as smoke, flags, or windsocks to identify wind direction.
- Overcorrection: Overcorrection is a common error in drift correction. It occurs when you make a correction that is too large, resulting in a deviation in the opposite direction. To correct this, reduce the correction and make small adjustments until you achieve the desired result.
- Inadequate correction: Inadequate correction is the opposite of overcorrection. It occurs when you make a correction that is too small, resulting in continued drift. To correct this, increase the correction gradually until you achieve the desired result.
Coordination
Coordination is critical in ground reference maneuvers. Failure to coordinate your controls can result in uncoordinated flight, which can lead to a loss of control. The following are common errors and corrections in coordination:
- Inadequate rudder input: Inadequate rudder input is a common error in coordination. It occurs when you fail to apply sufficient rudder to maintain coordination. To correct this, increase the rudder input gradually until you achieve coordination.
- Overuse of ailerons: Overuse of ailerons is another common error in coordination. It occurs when you use too much aileron to turn the aircraft, resulting in adverse yaw. To correct this, reduce the aileron input and increase the rudder input to maintain coordination.
Situational Awareness
Situational awareness is critical in ground reference maneuvers. Failure to maintain situational awareness can result in a loss of control or deviation from the intended path. The following are common errors and corrections in situational awareness:
- Failure to scan for traffic: Failure to scan for traffic is a common error in situational awareness. It occurs when you fail to scan for other aircraft or obstacles in your path. To correct this, establish a scanning pattern and scan for traffic regularly.
- Tunnel vision: Tunnel vision is another common error in situational awareness. It occurs when you focus on one aspect of the maneuver and fail to monitor other critical factors. To correct this, maintain a broad focus and monitor all critical factors.
Wind Drift Correction
Wind drift correction is essential in ground reference maneuvers. Failure to correct for wind drift can result in significant deviations from your intended path. The following are common errors and corrections in wind drift correction:
- Failure to anticipate wind drift: Failure to anticipate wind drift is a common error in wind drift correction. It occurs when you fail to anticipate the effect of wind on your aircraft. To correct this, anticipate the effect of wind on your aircraft and adjust your heading accordingly.
- Failure to adjust for wind changes: Failure to adjust for wind changes is another common error in wind drift correction. It occurs when you fail to adjust your heading when the wind changes. To correct this, monitor the wind direction and adjust your heading as necessary.
Conclusion
Ground reference maneuvers are essential for any pilot who wants to improve their flying skills. These maneuvers allow you to develop a better understanding of your aircraft's performance, as well as your own capabilities as a pilot. By mastering these maneuvers, you will be better equipped to handle a variety of situations while flying.
To perform these maneuvers successfully, you must have a solid understanding of your aircraft's performance capabilities, as well as the effects of wind and other environmental factors on your flight. You must also be able to maintain a constant altitude, airspeed, and bank angle throughout the maneuver.
In addition to improving your flying skills, ground reference maneuvers are also an excellent way to build your confidence as a pilot. By practicing these maneuvers regularly, you will develop the muscle memory and situational awareness necessary to handle unexpected situations while flying.
Overall, ground reference maneuvers are an essential part of any pilot's training. By mastering these maneuvers, you will become a safer, more confident, and more skilled pilot, capable of handling a wide range of flying conditions.
Frequently Asked Questions
1 - What are the three types of maneuvers required for a private pilot checkride?
The three types of maneuvers required for a private pilot checkride are:
- Ground Reference Maneuvers
- Flight at Slow Airspeeds
- Basic Instrument Maneuvers
2 - Do you do clearing turns for ground reference maneuvers?
Yes, you should always do clearing turns before starting any maneuver. This ensures that the area is clear of other aircraft and hazards.
3 - What is the IMSAFE checklist and why is it important for ground reference maneuvers?
The IMSAFE checklist is a pre-flight checklist that pilots use to assess their own fitness to fly. It stands for:
- Illness
- Medication
- Stress
- Alcohol
- Fatigue
- Emotion
It is important to use the IMSAFE checklist before performing ground reference maneuvers to ensure that you are mentally and physically prepared for the flight.